
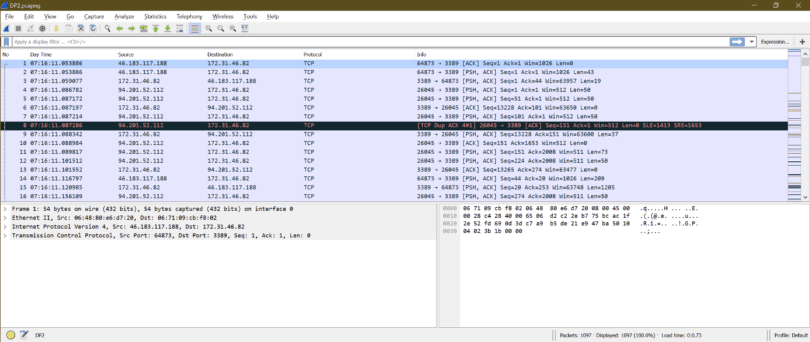
You can also export to XML, PostScript®, CSV, or plain text. Read/write many different capture file formats: tcpdump (libpcap), Pcap NG, WildPackets EtherPeek/TokenPeek/AiroPeek … it’s a long list.
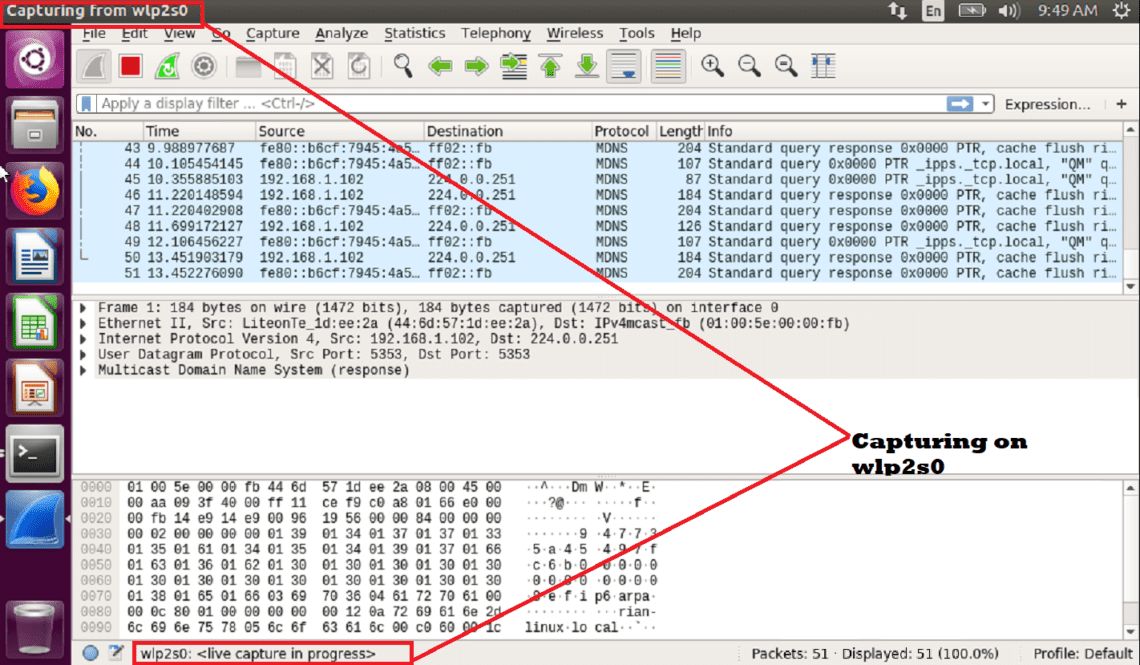
Captured network data can be browsed via a GUI or via the TTY-mode TShark utility.Live capture and offline analysis with powerful display filters.Deep inspection of hundreds of protocols, with more being added all the time.Nslookup -debug -type=aaaa clay.ns.cloudflare. In this final example, look up for TTL for ‘AAAA’ record for ‘using authoritative name server named ‘clay.ns.’ First, open a command prompt window by visiting Start > Command Prompt (also called as cmd.exe) and type the following command: A note about Windows users to find Time-To-Live (TTL) DNS record
See Time-To-Live (TTL) is now defined in a nice format such as 1d (one day) or 5h42m51s (five hourse 42 mintues and 51 seconds) for given DNS record. Pass the +ttlunits as follows to display the TTL in friendly human-readable time units of “s”, “m”, “h”, “d”, and “w”, representing seconds, minutes, hours, days and weeks:ĭig +nocmd +noall +answer +ttlunits A dig +nocmd +noall +answer +ttlunits MX ĭig +nocmd +noall +answer +ttlunits NS How to get friendly human-readable time units for my TTL However, if you need just the TTL value, you can try the following syntax:ĭig +nocmd +noall +answer +ttlid A dig +nocmd +noall +answer +ttlid AAAA dig +nocmd +noall +answer +ttlid MX So far, all examples give out a long answer from the dig.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
